jQuery DataTables is a table component that is powerful for data management. These plugins provide searching, sorting, pagination, filter per column, and many more. But we have some problems combining jQuery Datatables and Laravel framework.
We separate applications (Rest API and User Interface). For Rest API we use Laravel Framework and for User Interface use Laravel too, but we only Blade component and Guzzle as HTTP Client Library.
We now Laravel has good packages for handle it, as far I know Yajra’s good and incredible packages (you can see Yajra’s package on Github). But using Yajra’s library was not possible at that time, because Yajra was using Eloquent and can’t use HTTP Client (like Guzzle, UniRest, etc). Then we do research to deal with this problem and got results as we would discuss in this post.
On these tutorials, we use an empty Laravel 6.x project with Bootstrap 3, jQuery Datatables plugins. Our goal in this tutorial is to Display User Lists in Datatables (Searching and Sorting also). Ok let’s start the codings.
Integrated jQuery Datatables and Laravel Framework
First Step
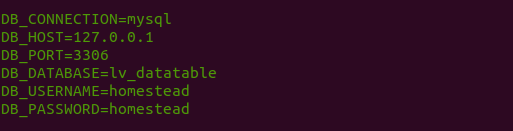
Setup the database connection on your Laravel .env. like this
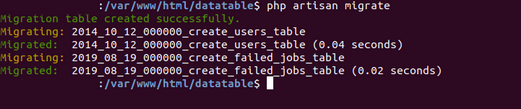
After that, run database migration and create 100 dummy records using the Faker library, Ok open your Terminal then run step by step this command
Run Laravel migration by typing a command
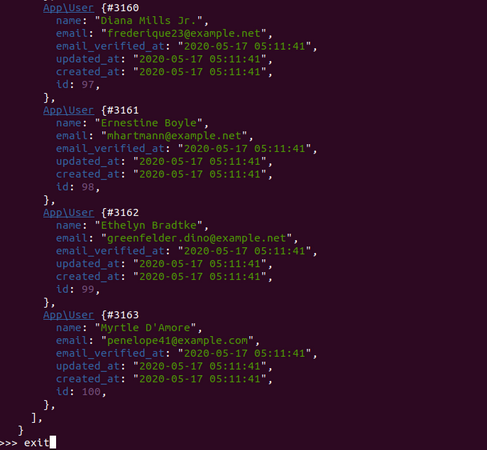
Run Laravel tinker by typing a command
Results of Laravel Tinker
Ok, the tables and data dummy creation are already completed, The next step is to make a new controller using a command line.
Step Two
Create a new controller, in this tutorial we created a UserController
|
1 |
php artisan make:controller UserController |
Open the UserController and add an index method.
The method above is very simple, which functions are only to display the index page. After you create a method, the next step is to register the index method to the Laravel’s routing.
Step Three
Open and edit the file routes/web.php, and add this route
|
1 |
Route::get('/datatable', 'UserController@index')->name('datatable'); |
Step Four
Make a View in resources/views/user folder and name it index.blade.php. After you created it we need to create an HTML table and a jQuery Datatables scripts on it. Use the snippet code below for the table.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
<!-- DATATABLE --> <table id="user_table" class="table table-striped table-bordered" width="100%"> <thead> <tr> <th>No</th> <th style="visibility: hidden">Id</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Email</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody></tbody> </table> |
The above code has no special needs, it’s just that you need to make sure the table id is the same as id on the javascript code. After we create a table, the next step is to create a jQuery Datatables codes, the code is like this
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
$('#user_table').DataTable({ processing: true, serverSide: true, responsive: true, ajax: { "url": "{{ url('/showDatatables') }}", "type": "GET" }, columns: [ { data: 'no', name: 'no', width: '5%', className: 'center' }, { data: 'id', name: 'id', width: '5%', visible: false, className: 'center' }, {data: 'name', name: 'name'}, {data: 'email', name: 'email'} ], order: [[1, "asc"]], columnDefs: [ {targets: 0, sortable: false, orderable: false}, {targets: 1, orderable: false}, {targets: 2, sortable: true, orderable: true} ], }); |
On line 104 in the code above, we add a URL to retrieve data from the UserController, with the URL prefix being ‘/getDatatable’. The full code is as follows, *noted we use the Laravel 5.2.x template because it still uses purely a blade (not vue.js template)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Odenktools</title> <!-- Fonts --> <link rel="stylesheet" href="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/4.5.0/css/font-awesome.min.css" integrity="sha384-XdYbMnZ/QjLh6iI4ogqCTaIjrFk87ip+ekIjefZch0Y+PvJ8CDYtEs1ipDmPorQ+" crossorigin="anonymous"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Lato:100,300,400,700"> <!-- Styles --> <link rel="stylesheet" href="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.6/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-1q8mTJOASx8j1Au+a5WDVnPi2lkFfwwEAa8hDDdjZlpLegxhjVME1fgjWPGmkzs7" crossorigin="anonymous"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="//cdn.datatables.net/1.10.21/css/dataTables.bootstrap.min.css" crossorigin="anonymous"> <style> body { font-family: 'Lato'; } .fa-btn { margin-right: 6px; } </style> </head> <body id="app-layout"> <nav class="navbar navbar-default navbar-static-top"> <div class="container"> <div class="navbar-header"> <!-- Collapsed Hamburger --> <button type="button" class="navbar-toggle collapsed" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#app-navbar-collapse"> <span class="sr-only">Toggle Navigation</span> <span class="icon-bar"></span> <span class="icon-bar"></span> <span class="icon-bar"></span> </button> <!-- Branding Image --> <a class="navbar-brand" href="{{ url('/') }}"> Odenktools </a> </div> <div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="app-navbar-collapse"> <!-- Left Side Of Navbar --> <ul class="nav navbar-nav"> <li><a href="{{ url('/home') }}">Home</a></li> </ul> </div> </div> </nav> <div class="container"> <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2"> <div class="panel panel-default"> <!-- DATATABLE --> <table id="user_table" class="table table-striped table-bordered" width="100%"> <thead> <tr> <th>No</th> <th style="visibility: hidden">Id</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Email</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody></tbody> </table> </div> </div> </div> </div> <!-- jQuery --> <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/2.2.3/jquery.min.js" integrity="sha384-I6F5OKECLVtK/BL+8iSLDEHowSAfUo76ZL9+kGAgTRdiByINKJaqTPH/QVNS1VDb" crossorigin="anonymous"></script> <!-- bootstrap --> <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.6/js/bootstrap.min.js" integrity="sha384-0mSbJDEHialfmuBBQP6A4Qrprq5OVfW37PRR3j5ELqxss1yVqOtnepnHVP9aJ7xS" crossorigin="anonymous"></script> <!-- jquery datatable --> <script src="//cdn.datatables.net/1.10.21/js/jquery.dataTables.min.js"></script> <script src="//cdn.datatables.net/1.10.21/js/dataTables.bootstrap.min.js"></script> <!-- SCRIPT DATATABLE HERE --> <script> $('#user_table').DataTable({ processing: true, serverSide: true, responsive: true, ajax: { "url": "{{ url('/getDatatable') }}", "type": "GET" }, columns: [ { data: 'no', name: 'no', width: '5%', className: 'center' }, { data: 'id', name: 'id', width: '5%', visible: false, className: 'center' }, {data: 'name', name: 'name'}, {data: 'email', name: 'email'} ], order: [[1, "asc"]], columnDefs: [ {targets: 0, sortable: false, orderable: false}, {targets: 1, orderable: false}, {targets: 2, sortable: true, orderable: true}, ], }); </script> </body> </html> |
in the code above I added Bootstrap 3 and jQuery Datatables plugins. if it turns out you already use Bootstrap 4, you can change the script and style at cdn.datatables.net, then you choose the styling options based on your needs. The code for the View is now finished, we can proceed to the next step.
Step Five (Final Steps)
In the UserController we add a method named getDatatable, what is the function? well, its function is to get data from the users table in your database.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 |
/** * Build datatable json */ public function getDatatable(\Illuminate\Http\Request $request) { try { // -- START DEFAULT DATATABLE QUERY PARAMETER $draw = $request->input('draw'); $start = $request->input('start'); $length = $request->input('length'); $page = (int)$start > 0 ? ($start / $length) + 1 : 1; $limit = (int)$length > 0 ? $length : 10; $columnIndex = $request->input('order')[0]['column']; // Column index $columnName = $request->input('columns')[$columnIndex]['data']; // Column name $columnSortOrder = $request->input('order')[0]['dir']; // asc or desc value $searchValue = $request->input('search')['value']; // Search value from datatable //-- END DEFAULT DATATABLE QUERY PARAMETER //-- START DYNAMIC QUERY BINDING $conditions = '1 = 1'; if (!empty($searchValue)) { $conditions .= " AND name LIKE '%" . trim($searchValue) . "%'"; $conditions .= " OR email LIKE '%" . trim($searchValue) . "%'"; } //-- END DYNAMIC QUERY BINDING //-- WE MUST HAVE COUNT ALL RECORDS WITHOUT ANY FILTERS $countAll = \App\User::count(); //-- CREATE LARAVEL PAGINATION $paginate = \App\User::select('*') ->whereRaw($conditions) ->orderBy($columnName, $columnSortOrder) ->paginate($limit, ["*"], 'page', $page); $num = 1; $items = array(); foreach ($paginate->items() as $idx => $row) { $items[] = array( "no" => $num, "id" => $row['id'], "name" => $row['name'], "email" => $row['email'], ); $num++; } //-- START CREATE JSON RESPONSE FOR DATATABLES $response = array( "draw" => (int)$draw, "recordsTotal" => (int)$countAll, "recordsFiltered" => (int)$paginate->total(), "data" => $items ); return response()->json($response); //-- END CREATE JSON RESPONSE FOR DATATABLES } catch (\Exception $e) { // Error Log \Illuminate\Support\Facades\Log::error($e->getMessage()); return abort(404); } } |
Is the code length too long? Yup, a little long is okay as long as it has a powerful function. we discussed the code above step by step, but if you want to take action please scroll to the bottom. Let’s start codes explain
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
// -- START DEFAULT DATATABLE QUERY PARAMETER $draw = $request->input('draw'); $start = $request->input('start'); $length = $request->input('length'); $page = (int)$start > 0 ? ($start / $length) + 1 : 1; $limit = (int)$length > 0 ? $length : 10; $columnIndex = $request->input('order')[0]['column']; // Column index $columnName = $request->input('columns')[$columnIndex]['data']; // Column name $columnSortOrder = $request->input('order')[0]['dir']; // asc or desc value $searchValue = $request->input('search')['value']; // Search value from datatable //-- END DEFAULT DATATABLE QUERY PARAMETER |
The code blocks above are the default parameters sent by the jQuery Datatables :
$start is the position from which the data will be displayed (default parameter from Datatables).
$length is how much data will be displayed (default parameter from Datatables).
$page is a calculation prefix for Laravel’s pagination, it is also used to provide a default value if the parameter is not sent by the Datatables.
$limit is a calculation prefix for Laravel’s pagination, it is also used to provide a default value if the parameter is not sent by the Datatables.
$columnName is the name of the column in the Datatables, this value is usually used if you are searching based on the column name provided.
$columnSortOrder variable is used to sort either Ascending or Descending based on the selected column.
$searchValue variable is used to find data.
Okay, we scroll down a little, there is a code
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
$conditions = '1 = 1'; if (!empty($searchValue)) { $conditions .= " AND name LIKE '%" . strtolower(trim($searchValue)) . "%'"; $conditions .= " OR email LIKE '%" . strtolower(trim($searchValue)) . "%'"; } |
The code is used so that the Datatables can search for data in the column name or also the email column in the users table. In the code, there is a condition 1 = 1, it is a hack so that if the Datatables is not sending the search parameter our controller will not display an error. So by default Laravel will generate SQL queries like this :
|
1 |
select * from "users" where 1 = 1 |
and if we do a search data, Laravel will generate an SQL query like this:
|
1 |
select * from "users" where 1 = 1 AND nme LIKE '%john%' OR email LIKE '%john%'; |
Lovely hack right? continue scrolling down again, there is a code
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
//-- WE MUST HAVE COUNT ALL RECORDS WITHOUT ANY FILTERS $countAll = \App\User::count(); //-- CREATE DEFAULT LARAVEL PAGING $paginate = \App\User::select('*') ->whereRaw($conditions) ->orderBy($columnName, $columnSortOrder) ->paginate($limit, ["*"], 'page', $page); $num = 1; $items = array(); foreach ($paginate->items() as $idx => $row) { $items[] = array( "no" => $num, "id" => $row['id'], "name" => $row['name'], "email" => $row['email'], ); $num++; } //-- START CREATE JSON RESPONSE FOR DATATABLES $response = array( "draw" => (int)$draw, "recordsTotal" => (int)$countAll, "recordsFiltered" => (int)$paginate->total(), "data" => $items ); |
$countAll is the variable needed by the Datatables to count the total number of records in the users table.
$paginate is a variable to paginate from Laravel, this code block does not need to be changed (maybe only the SELECT (‘*’) that need to be changed to optimize the query time results)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
$num = 1; $items = array(); foreach ($paginate->items() as $idx => $row) { $items[] = array( "no" => $num, "id" => $row['id'], "name" => $row['name'], "email" => $row['email'], ); $num++; } |
The code above works for displaying some columns in the Datatables, in these tutorials we will display 4 columns
- no
- id
- name
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
//-- START CREATE JSON RESPONSE FOR DATATABLES $response = array( "draw" => (int)$draw, "recordsTotal" => (int)$countAll, "recordsFiltered" => (int)$paginate->total(), "data" => $items ); |
and the last is the $response variable, the code is the output rules required by the jquery Datatables plugin, so we have to follow it and don’t need to change anything.
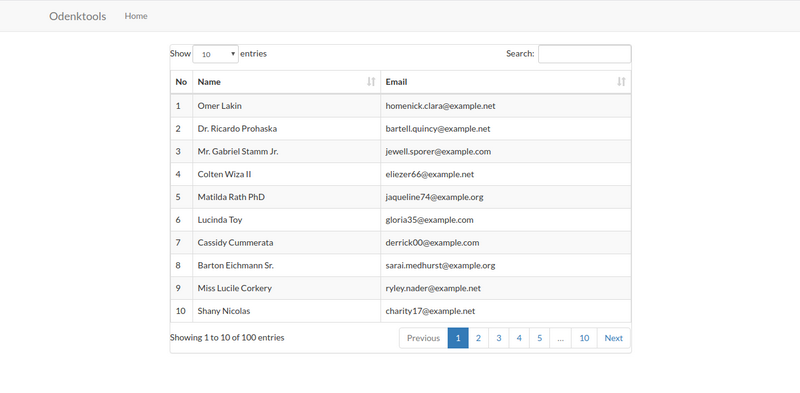
And finally, onto the final stage. Curious as to what the results are? please open your browser and navigate to the URL
HTTP://{{HOST_ANDA}}/datatable
Do you see any results? if so, do a data Searching and also Sorting the Datatables column, does it work? if it is CONGRATULATIONS! and I need to inform you about the code, the sample code above is production-ready, so it is safe to use the code above if you have a project or product.
 This is the end of the first tutorial. too long huh? but satisfied with the results right? you don’t need plugins and so on to do this. honestly, I think it’s a little hard to fix people’s code if there’s a bug in someone’s package. so if you can do it by yourself why use someone else’s package? See you in the next tutorials!
This is the end of the first tutorial. too long huh? but satisfied with the results right? you don’t need plugins and so on to do this. honestly, I think it’s a little hard to fix people’s code if there’s a bug in someone’s package. so if you can do it by yourself why use someone else’s package? See you in the next tutorials!